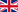
Chorionic villus(trophoblast) sampling
/What it is and when it happens
Taking trophoblast (or taking chorionic villus) is an invasive prenatal diagnosis performed in the first trimester, from the 12th to the 14th week of gestation, if there are indications

Trophoblast epithelium taking includes examination of chorionic villi (small portions of the placenta being formed). The embryo and the placenta have common cytological origin, so placental cell chromosomes can be used to control embryo chromosomes.
Indications
- First response to advanced pregnancy (after the 35th year)
- Pathological examination of cervical translucency
- Suspicious ultrasound findings
- Previous pregnancy with a history of pregnant fetus
- Parents who are carriers of diseases such as Mediterranean anemia, fibrocystic disease and others.
- Wishes of the pregnant woman, due to excessive anxiety about any chromosomal anomalies.
TECHNICAL TAKING TROFOVLASTIS
The CVS is transabdominally and sometimes transvaginal.
In the case of transabdominally discharge, a local anesthetic is administered to the abdominal wall and then a fine needle passes the abdominal and uterine wall by removing a small sample of chorionic villi. In the case of the transvaginal approach, the needle is inserted through the cervix following the administration of antisepsis. In both cases, the needle is continuously monitored ultrasound to prevent possible fetal injury. The whole process takes a few minutes and is then controlled by the cardiac function of the fetus.
Results
The first results come in 2 days with a rapid PCR analysis, which gives us results for syndromes, trisomy 21, trisomy 18 (Edwards), trisomy 13-15 (Patau) and Turner, and recognizes its shelf embryo. We have the complete results in 10-15 days, with the fetal cell culture controlling the entire karyotype of the fetus. At the same time, the gene (ΔF508) of cystic fibrosis is controlled. The reliability of the results reaches 99.9%. In a very small percentage, falsely positive results can be given (i.e., an abnormality of the fetus is indicated without this being true), as in the case of mosaic, which requires further amniocentesis control.
Dangers
Taking trophoblast can lead to complications at a rate of 0.5-1%.
These include endometrial infection (with concomitant fever) and eradication of the fetus, manifested by the onset of uterine contractions, amniotic fluid loss and vaginal haemorrhage. If these symptoms occur, the woman should contact her doctor immediately.
Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is one of the most well-known shots from the "embryonic unit". The experience at "ELEFTHO oe" is great, over two thousand downloads have been done over time.
It is an invasive method whereby a fine needle and under continuous ultrasound checkup enter the amniotic cavity and draw a small amount (about 15-20ml) of amniotic fluid. In this fluid cells are isolated from fetal tissues such as skin, gastrointestinal tract or respiratory tract which are examined in the genetics laboratory for chromosomal abnormalities, genetic diseases, metabolic diseases and a set of factors that can affect fetal health.
The process is painless and local anesthetic is not used. This contributes to the fact that the needle we use is very thin and the area where the amniocentesis occurs has fewer nerve ends that detect pain.

Generally we can say that amniocarcerosis is a method of obtaining from the "embryonic unit" which:
It hurts less than a simple blood sampling, it takes little time, there is no risk of injury to the fetus and the needle entry becomes under ultrasound monitoring, the point of entry into the amniotic sac closes immediately and the amniotic fluid is rapidly replaced by the fetus.
When is it done?
Amniocentesis is performed from the 16th week onwards but not in the advanced week of pregnancy because the fetal cells are greatly reduced and the treatment is difficult in the lab.
Why is it done?
- For the diagnosis of numerical chromosomal abnormalities e.g. Down syndrome
- For the diagnosis of genetic syndromes
- For the diagnosis of hereditary disorders e.g. Mediterranean anemia or cystic fibrosis
- For the diagnosis of congenital infections e.g. toxoplasmosis, MCV, etc.
With the advancement of genetics and the introduction of molecular karyotype, we can now detect with invasive control more than 150 rare genetic syndromes.
What are the risks?
There is a 1/300 chance of miscarriage after an invasive examination. Elimination can be due to membrane rupture or infection.
What precautions should we take after?
It is usually enough to stay bedrriden and restrict physical activity for two days. Preventive antibiotic is given for 4 days.
The results of amniocentesis?
They are given in three stages:
PCR in one day
The result by PCR method looks for Down syndrome (trisomy 21), Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18), Patau syndrome (trisomy 13) and Turner syndrome. An answer is also given if the embryo bears the most common ΔF508 mutation for cystic fibrosis.
Molecular karyotype in 1 week
This technique examines the embryo genome very accurately and more than 150 rare genetic syndromes are detected.
Cell culture in 2 weeks
It complements the molecular karyotype.
Amniocentesis is a safe examination in experienced hands. However, as there is a small risk of miscarriage, a discussion should be made after a briefing of the future parents to make a responsible decision.